Microsoft SQL Server
The SQL Server integration synchronizes metadata from your SQL Server databases into the data lineage graph.
Web App
Fields
| Field | Value | Example |
|---|---|---|
| source | The name of the source, see sources | my-source |
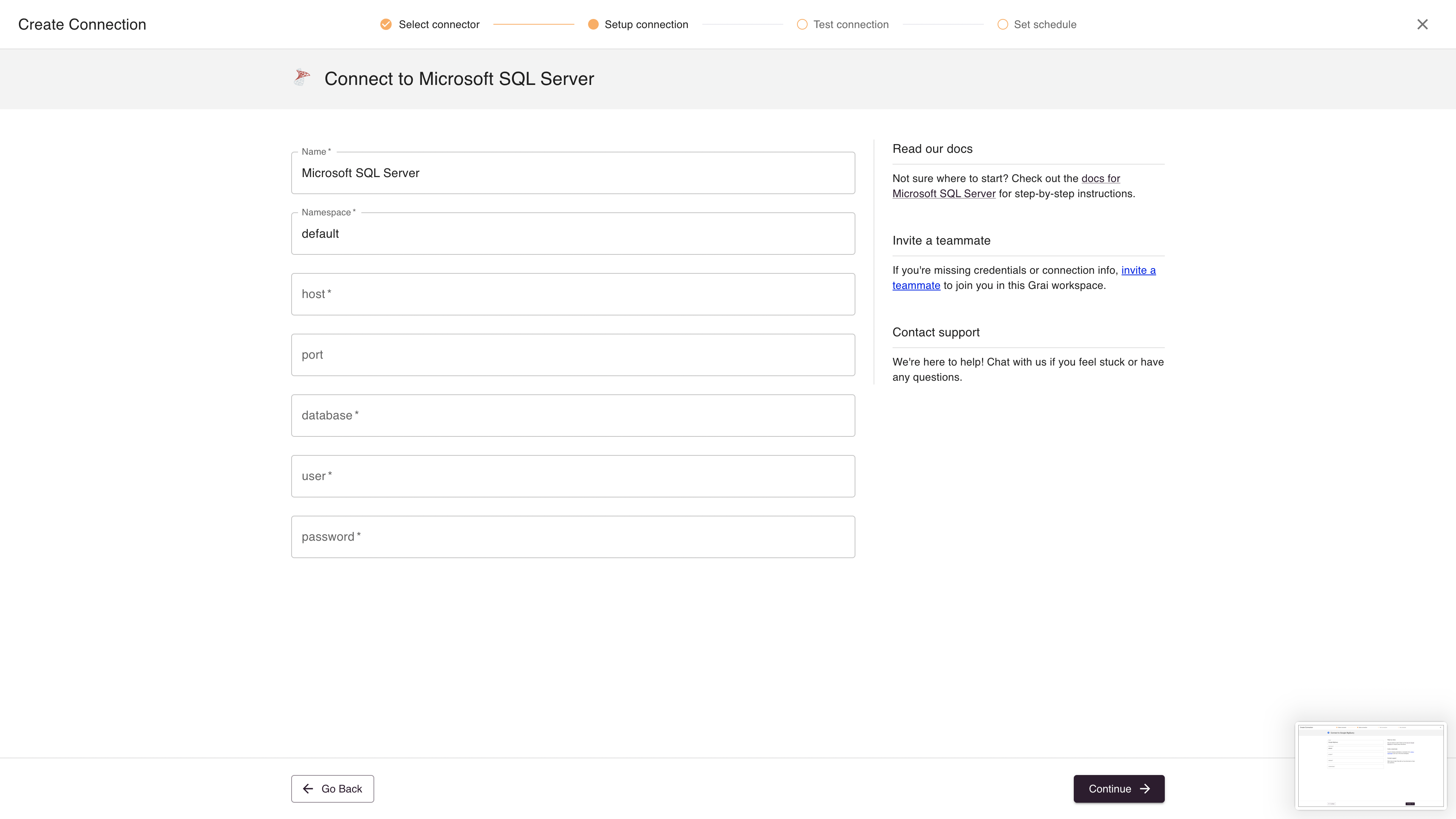
| Name | Name for connection | Microsoft SQL Server |
| Namespace | Namespace for the connection, see namespaces | default |
| host | Database host | sample-database.cudyk77thtpt.us-west-2.rds.amazonaws.com |
| port | Database port | 5432 |
| database | Database name | jaffle_shop |
| user | Database user | |
| password | Database password |
Your database will need to be accessible from wherever you are running the Grai server. If you are using Grai Cloud your database will need to be accessible from the internet.
Python Library
Installation
You'll need to first install the ODBC drivers for SQL Server before installing the SQL Server integration.
If you're on a mac these can be installed with brew install unixodbc. If
you're using Apple Silicon and encounter any issues running or installing the
drivers we have some additional support documentation
here (opens in a new tab)
pip install grai_source_mssqlMore information about the API is available here.
Example
The library is split into a few distinct functions but if you only wish to extract nodes/edges you can do so as follows:
from grai_source_mssql import MsSQLIntegration
from grai_schemas.v1.source import SourceV1
source = SourceV1(name="my-source", type="my-type")
mssql_params = {
"username": "my-username",
"password": "my-password",
"host": "my-mssql-hostname",
}
integration = MsSQLIntegration(source=source, namespace="mssql", **mssql_params)
nodes, edges = integration.get_nodes_and_edges()There are other option parameters like database, protocol, and port which are also available. More detail about ODBC connection string arguments are available from Microsoft (opens in a new tab)