Every aspect of Grai can be serialized to yaml. This allows you to manage your entire data lineage as code, backup your lineage in version control, or create and edit nodes/edges in code. You can find explicit yaml definitions for all Grai objects in the grai-schemas library. Documentation for the schemas can be found here.
Web App
The YAML File integration is used to upload a single YAML file, which needs to have the correct Grai format.
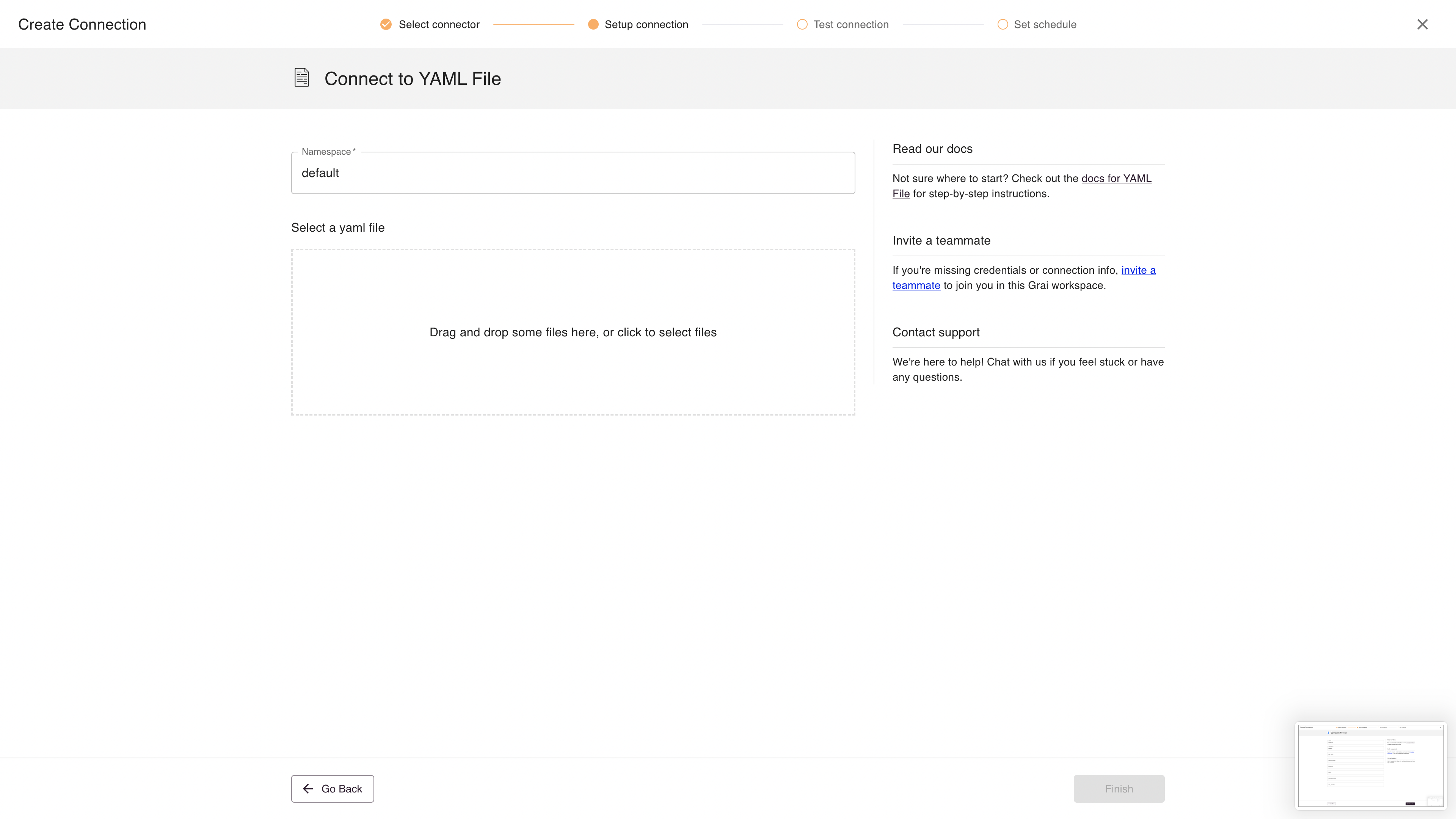
Fields
| Field | Value | Example |
|---|---|---|
| source | The name of the source, see sources | my-source |
| Namespace | Namespace for the connection, see namespaces | default |
CLI
You can create, edit, and delete lineage in yaml through the CLI.
Let's say you wanted to add an is_really_important flag to the metadata on the customer_id column of the customers table.
In that case we might write a yaml definition like this
type: Node
version: v1
spec:
name: "customers.customer_id"
namespace: default
is_active: true
metadata:
grai:
node_type: Column
is_really_important: trueWe could then update the server with this new information through the CLI
grai apply <node_file>You can do the same with edges
version: v1
type: Edge
spec:
source:
name: public.lineage_node.id
namespace: default
destination:
name: node2
namespace: test
is_active: true
metadata:
grai:
edge_type: "Edge"
stuff: goes_here